PRESENTATION
Published on June 16, 2015
Exhibit 99.1

A Case Study using Lectin - Affinity Plasmapheresis in the Treatment of Ebola Virus Disease Rod Kenley President, Aethlon Medical, Inc. 33rd Vicenza Course on Critical Care Nephrology June 12, 2015

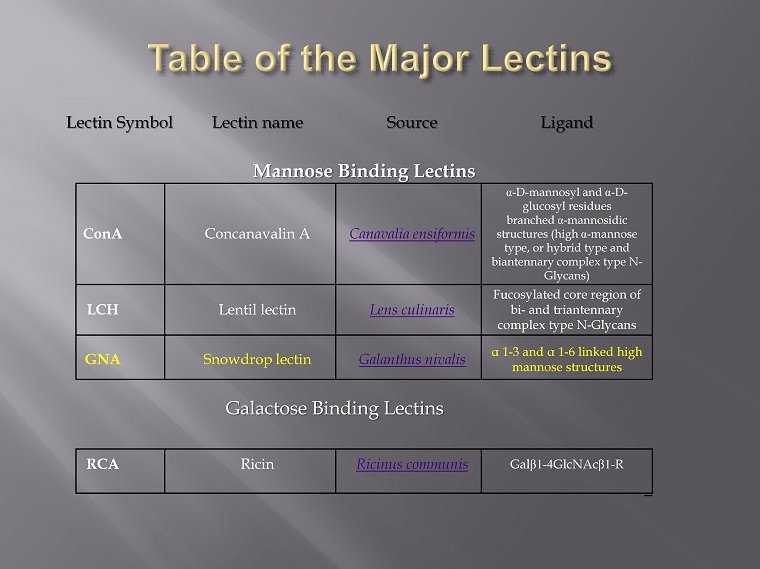
Lectin Symbol Lectin name Source Ligand Mannose Binding Lectins ConA Concanavalin A Canavalia ensiformis α - D - mannosyl and α - D - glucosyl residues branched α - mannosidic structures (high α - mannose type, or hybrid type and biantennary complex type N - Glycans ) LCH Lentil lectin Lens culinaris Fucosylated core region of bi - and triantennary complex type N - Glycans GNA Snowdrop lectin Galanthus nivalis α 1 - 3 and α 1 - 6 linked high mannose structures Galactose Binding Lectins RCA Ricin Ricinus communis Gal β1 - 4 GlcNAc β1 - R
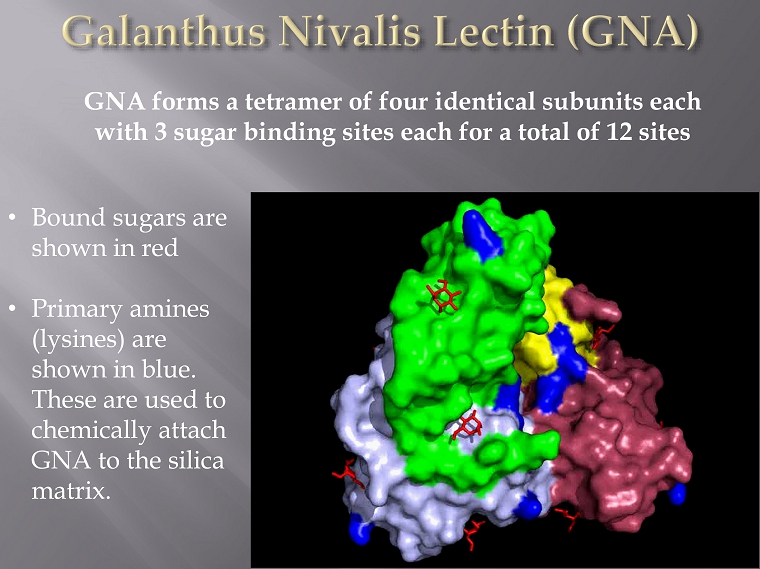
GNA forms a tetramer of four identical subunits each with 3 sugar binding sites each for a total of 12 sites • Bound sugars are shown in red • Primary amines ( lysines ) are shown in blue. These are used to chemically attach GNA to the silica matrix.

» Clearance of infectious viral pathogens » Clearance of shed glycoproteins
modified after Cook et al . and Dolnik et al .

© visual - science.ru GP1/2
Ebola (mut) – Ebola Zaire strain mutant; Ebola (wt) – Ebola Zaire strain Wild Type; Ebola (mac) – Ebola Zaire strain cultivated in Macrophages Capture of Ebola Virus by LAPD Ebola Removal from Tissue Culture Fluid (RT-PCR) 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 6 12 18 24 Time (hours) Copies/ml Ebola (mut) Ebola (wt) Ebola (mac) Studies were performed at CDC and USAMRIID
Clearance of sGP by LAPD 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (h) % Initial Density 1% 10% 100% 0 2 4 6 8 Time (h) % Initial Density Figure 1. Clearance of sGP by GNA Microkros from Reduced SDS/12% NuPAGE Western Blot. EBOVZ cell culture supernatant 5 ml passaged over GNA Microkros Hemopurifier at 1 ml/min. Detection via mouse anti sGP monoclonal (1:100) and goat anti mouse IgG (1:100) in blocking buffer visualized with TMB. Photographed with Eagle Eye system II and analyzed using ImageJ Figure 2. Clearance of sGP by GNA Microkros from Reduced SDS/12% Nupage Western Blot. EBOVZ cell culture supernatant 5ml passaged over GNA Microkros Hemopurifier at 1ml.min. Detection via mouse anti sGP monoclonal (1:100) and goat anti mouse IgG (1:100) in blocking buffer visualized with TMB. Photographed with Eagle Eye System II and analyzed using ImageJ. Studies were performed at CDC and USAMRIID
0% 50% 100% 150% 200% 250% 300% 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of Zero Time Time (hours) Expt Control Ebola removal from monkey plasma Studies were performed at CDC and USAMRIID
Capture of West Nile virus on LAPD Studies performed at Battelle Memorial Institute 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of virus remaining Time (hours) West Nile virus
Capture of H5N1 virus by LAPD Studies performed at Battelle Memorial Institute 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of virus remaining Time (hours) H5N1 (Bird Flu) virus
Capture of 1918 Flu virus by LAPD Studies performed at Battelle Memorial Institute 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of virus remaining Time (hours) Reconstructed 1918 Influenza virus
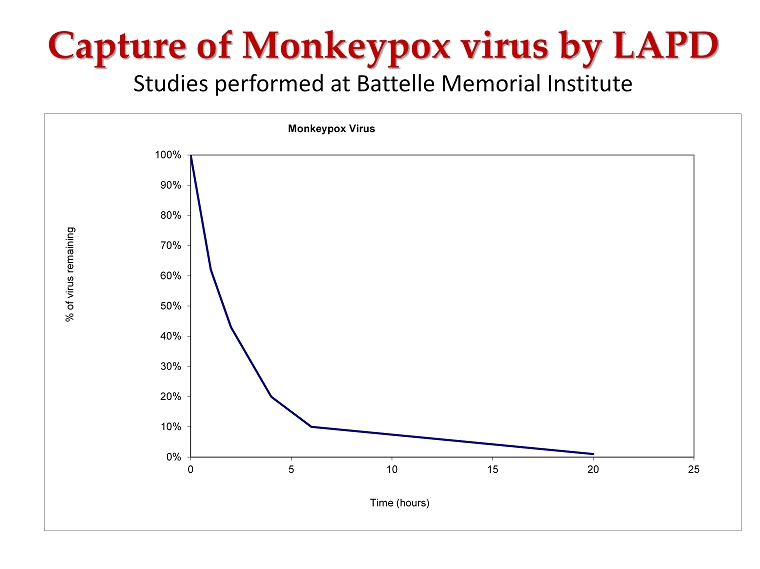
Capture of Monkeypox virus by LAPD Studies performed at Battelle Memorial Institute 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of virus remaining Time (hours) Monkeypox Virus
Clearance of H1N1 from Human Plasma Results: Pandemic H1N1/09 influenza virus was successfully removed from human plasma by the GNA - GAW lectin cartridge with a calculated half - time of 26.4 minutes. The control, in this case the regenerated cartridge re - filled with unmodified GAW 60 - 80 showed significantly slower removal. GNA-GAW T 1/2 = 26.4min Control GAW T 1/2 = 192.7min 0.0E+00 5.0E+04 1.0E+05 1.5E+05 2.0E+05 2.5E+05 3.0E+05 3.5E+05 4.0E+05 0 1 2 3 4 5 H1N1 copies/ml Time (hours) H1N1 Removal GNA-GAW Expt 1 GNA-GAW Expt 2 Unmodified GAW Control
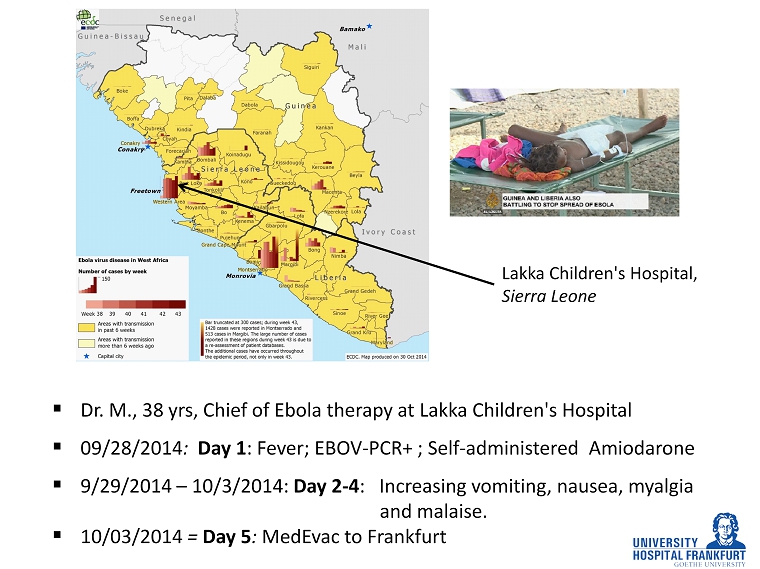
▪ Dr. M., 38 yrs, Chief of Ebola therapy at Lakka Children's Hospital ▪ 09/28/2014 : Day 1 : Fever; EBOV - PCR+ ; Self - administered Amiodarone ▪ 9/29/2014 – 10/3/2014: Day 2 - 4 : Increasing vomiting, nausea, myalgia and malaise. ▪ 10/03/2014 = Day 5 : MedEvac to Frankfurt Lakka Children's Hospital, Sierra Leone

▪ German Treatment Network for Highly Contagious and Life Threatening Diseases. ▪ 50 isolation unit beds (7 centers) ▪ 6 beds in Frankfurt (2 ICU ) Level A transport.

Therapeutic Options ▪ Unchanged since the 1967 VHF German outbreak: ▪ Best supportive care: Hydration, electrolyte balance, intensive care, convalescent serum. ▪ Organ failure support: Mechanical Respiration, TPN, CRRT. ▪ Drug: e.g. ZMAPP, FX - 06, faviripavir . ▪ Device: Extracorporeal virus and viral glycoprotein elimination by Lectin Affinity Plasmapheresis. Conventional Experimental
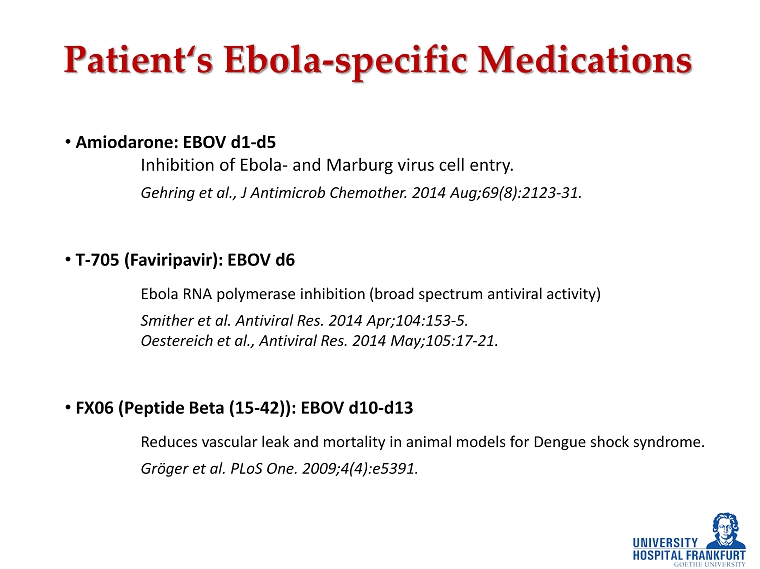
• Amiodarone: EBOV d1 - d5 Inhibition of Ebola - and Marburg virus cell entry. Gehring et al., J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Aug;69(8):2123 - 31. • T - 705 ( Faviripavir ): EBOV d6 Ebola RNA polymerase inhibition (broad spectrum antiviral activity) Smither et al. Antiviral Res. 2014 Apr;104:153 - 5. Oestereich et al., Antiviral Res. 2014 May;105:17 - 21. • FX06 (Peptide Beta (15 - 42)): EBOV d10 - d13 Reduces vascular leak and mortality in animal models for Dengue shock syndrome. Gröger et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5391. Patient‘s Ebola - specific Medications
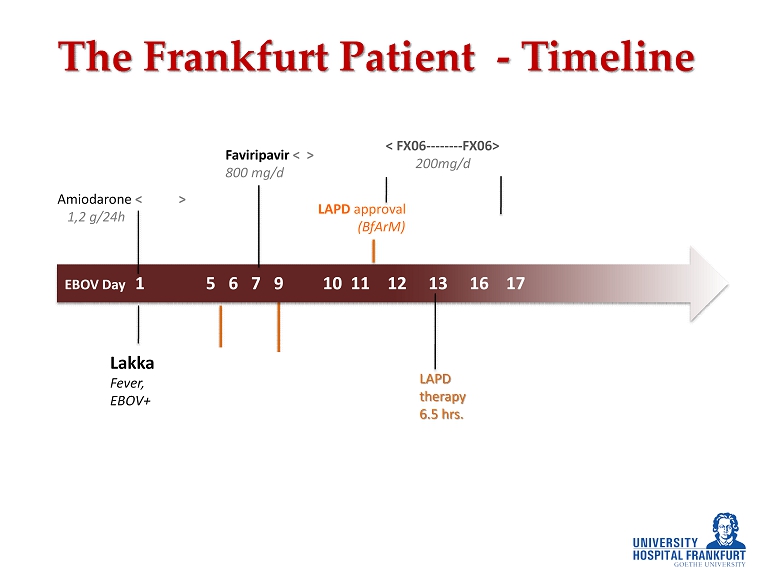
EBOV Day 1 5 6 7 9 10 11 12 13 16 17 The Frankfurt Patient - Timeline LAPD approval (BfArM) LAPD therapy 6.5 hrs. < FX06 -------- FX06> 200mg/d Viral load (Copies/ml) 10 7 10 7 10 7 4x10 5 Hb (g/dl) 12.6 8.1 Amiodarone < > 1,2 g/24h Faviripavir < > 800 mg/d Lakka Frankfurt CRRT Fever , Very weak , EBOV+ chills and fever
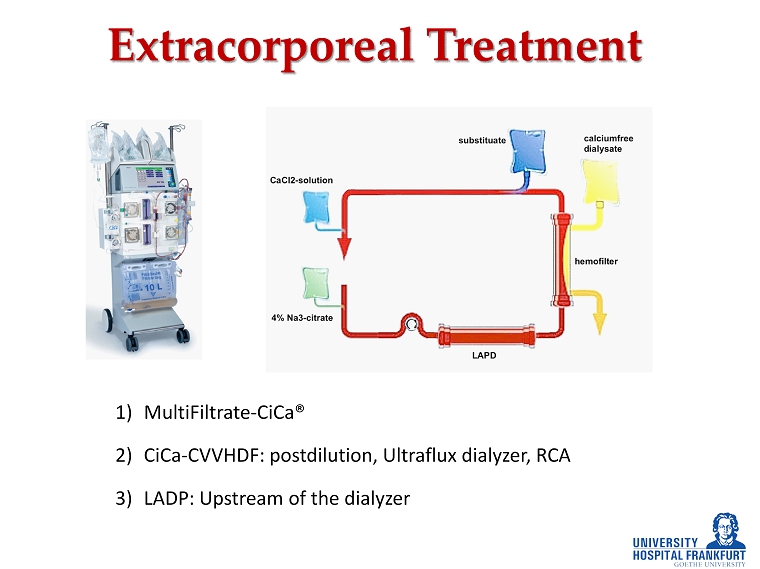
E xtracorporeal Treatment 1) MultiFiltrate - CiCa® 2) CiCa - CVVHDF: postdilution, Ultraflux dialyzer, RCA 3) LADP : Upstream of the dialyzer

Machine set - up
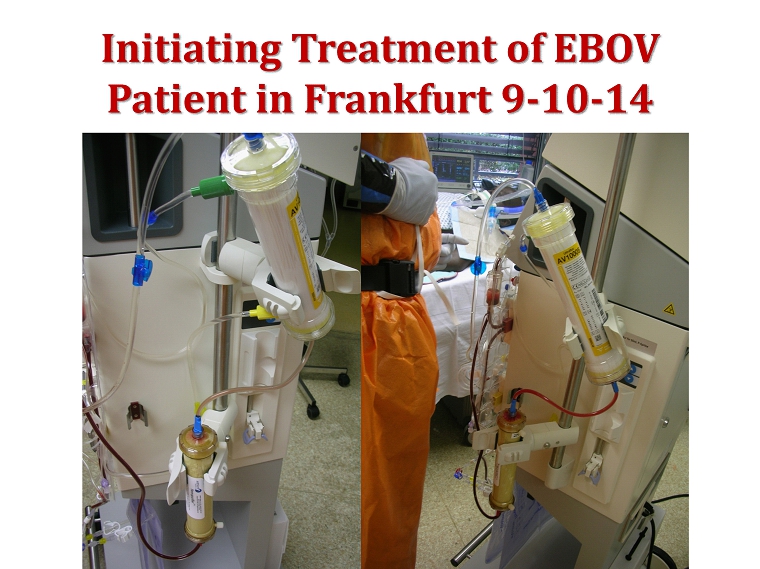
Initiating Treatment of EBOV Patient in Frankfurt 9 - 10 - 14
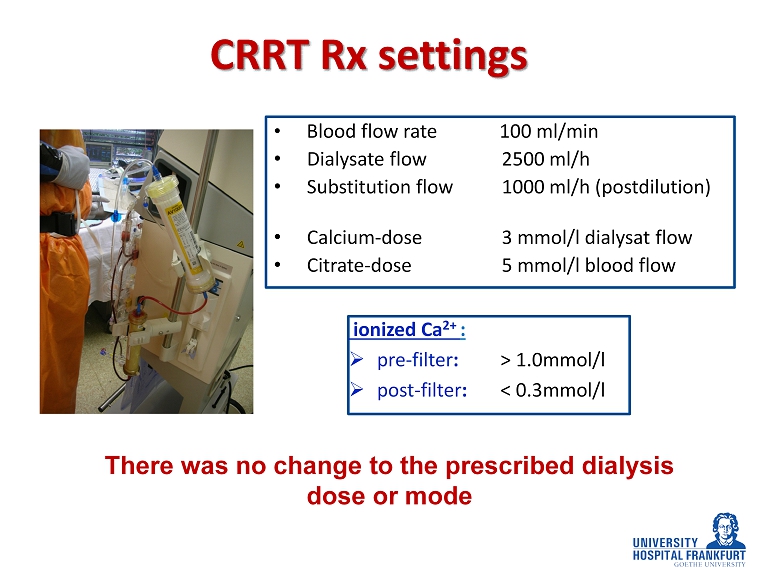
CRRT Rx settings • Blood flow rate 100 ml/min • Dialysate flow 2500 ml/h • Substitution flow 1000 ml/h (postdilution) • Calcium - dose 3 mmol/l dialysat flow • Citrate - dose 5 mmol/l blood flow There was no change to the prescribed dialysis dose or mode ionized Ca 2+ : » pre - filter : > 1.0mmol/l » post - filter : < 0.3mmol/l

LAPD Easily Extracted from Extracorporeal Circuit Stefan Büttner, MD

Phillips University BSL - 4 Facility Marburg Germany

Phillips University BSL - 4 Facility Marburg Germany
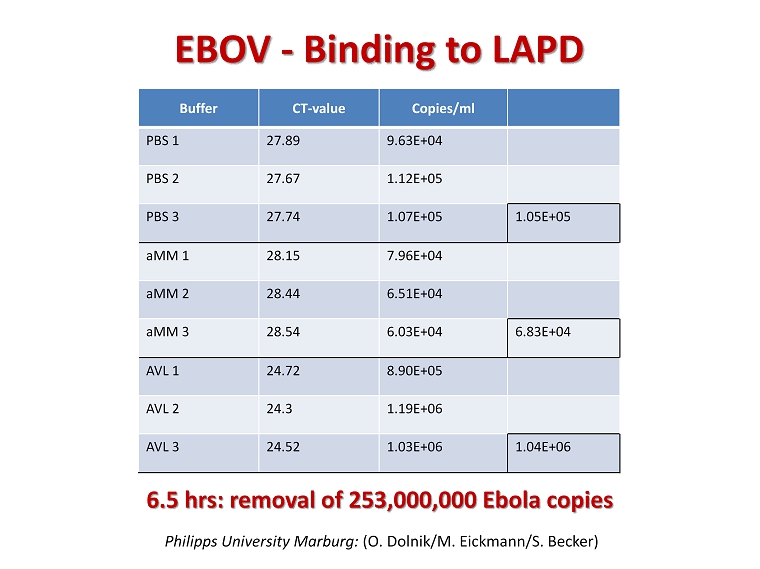
6.5 hrs : removal of 253,000,000 Ebola copies Philipps University Marburg: (O. Dolnik/M . Eickmann/S . Becker) EBOV - Binding to LAPD Buffer CT - value Copies/ml PBS 1 27.89 9.63E+04 PBS 2 27.67 1.12E+05 PBS 3 27.74 1.07E+05 1.05E+05 aMM 1 28.15 7.96E+04 aMM 2 28.44 6.51E+04 aMM 3 28.54 6.03E+04 6.83E+04 AVL 1 24.72 8.90E+05 AVL 2 24.3 1.19E+06 AVL 3 24.52 1.03E+06 1.04E+06
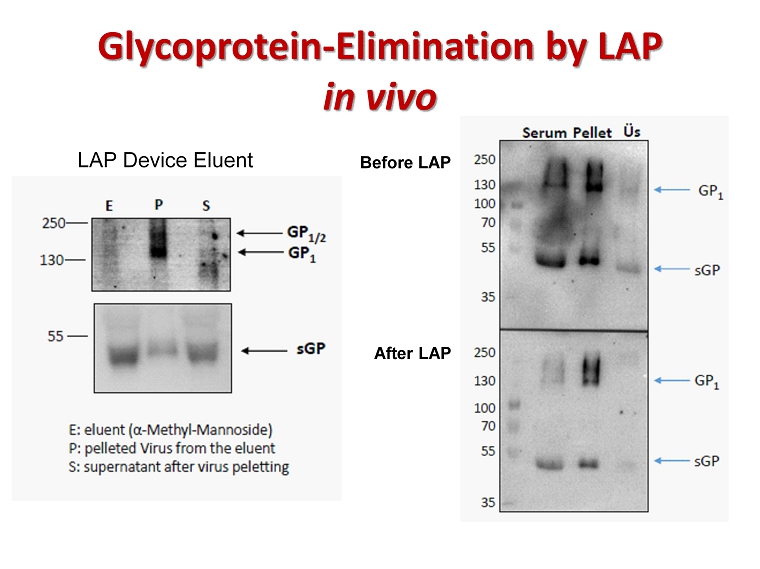
Glycoprotein - Elimination by LAP in vivo LAP Device Eluent Before LAP After LAP
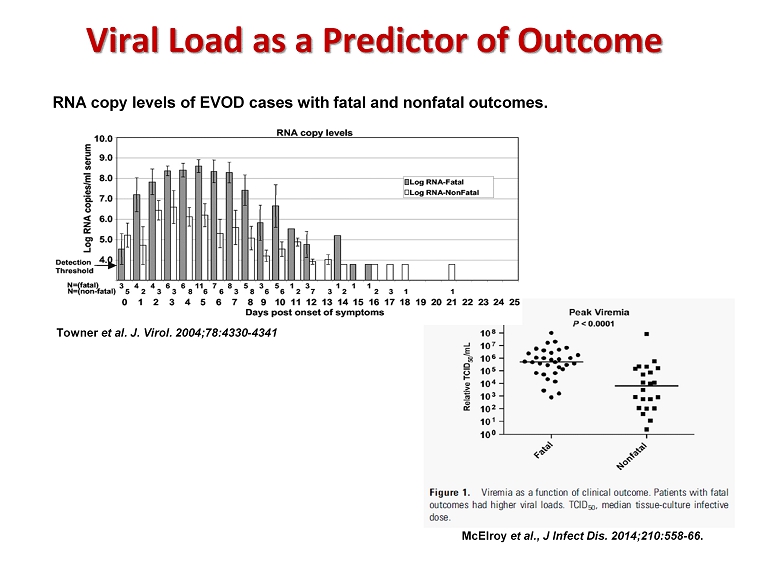
RNA copy levels of EVOD cases with fatal and nonfatal outcomes. Towner et al. J. Virol. 2004;78:4330 - 4341 McElroy et al., J Infect Dis. 2014;210:558 - 66 . Viral Load as a Predictor of Outcome
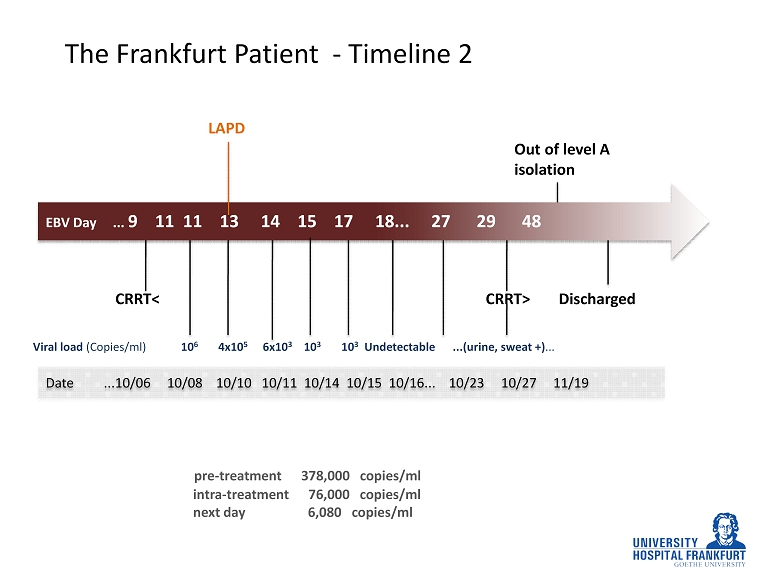
EBV Day ... 9 11 11 13 14 15 17 18... 27 29 48 The Frankfurt Patient - Timeline 2 LAPD CRRT< Out of level A isolation CRRT> pre - treatment 378,000 copies/ml intra - treatment 76,000 copies/ml next day 6,080 copies/ml Discharged Date ...10/06 10/08 10/10 10/11 10/14 10/15 10/16... 10/23 10/27 11/19 Viral load (Copies/ml) 10 6 4x10 5 6x10 3 10 3 10 3 Undetectable ...(urine, sweat +) ...

• No signs of hemolysis (low blood flow) • No clogging or clotting (regional citrate anticoagulation) • No allergic reaction • No adverse event during 6.5 hrs of treatment Safety of the Treatment

Conclusions » Lectin Affinity Plasmapheresis: – is safe and feasible – promising new supportive tool for severe Ebola infection » Hypotheses to explain therapeutic effect: – Reducing viral & glycoprotein load below “fatality threshold” reduces damage - buys time for supportive care/host defenses. – Reducing viral titer enhances antiviral drug bioavailability, enhancing effect while reducing toxicity and cost.

Acknowledgements Olga Dolnik ( Marburg) Helmut Geiger Markus Eickmann ( Marburg) Benjamin Koch Stefan Büttner
